December 30 2017
Coaching Meeting with Arne Scheuermann
& Research Process
Level I - Pre-Iconographic Analysis (of the Panofsky Method)
It is the formal and factual descriptions of what is seen in the visual (in this case the IS portraits), such as the colours, the content, and the format seen without any speculations.
It is a quantitative analysis of the photographs of the IS in Rumiyah (issues 1 to 13) by recording quantitative data through keywords.
During this session, Arne and I went over the keywords I had added on each 111 photos of the IS portraits from the Rumiyah magazine.
Pre-iconographic Analysis of the Islamic State fighters’ portraits in Rumiyah magazine:
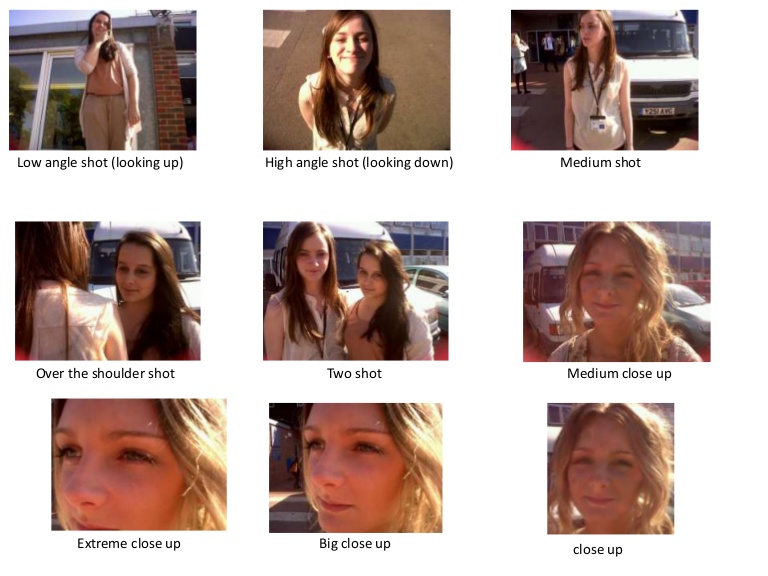
The keywords are categories according to what is seen in the photograph and the photography techniques used such as field size, camera angle, perspective, ratio, and so on. Figure 1.2 is an example of the pre-iconographic Analysis of 1 photo.
I decided not to add keywords to objects that were not clear as to what they were. I also decided to name a person ( - a fighter - if he is known such as Abou Bakr al-Baghdadi (see Figure 1.3)
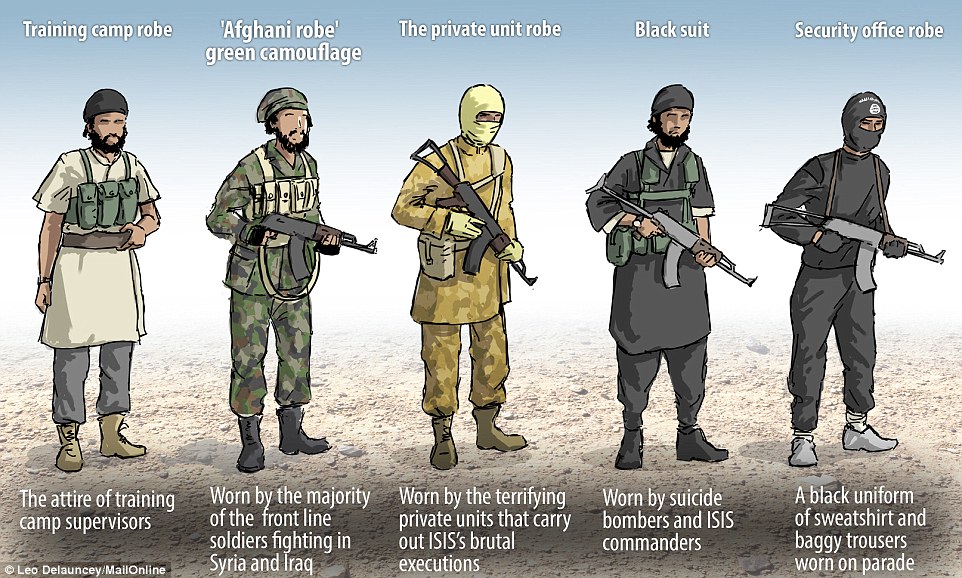
I had to search for some keywords in order to be able to describe them such as the military suits and robes (see Figure 1.1).
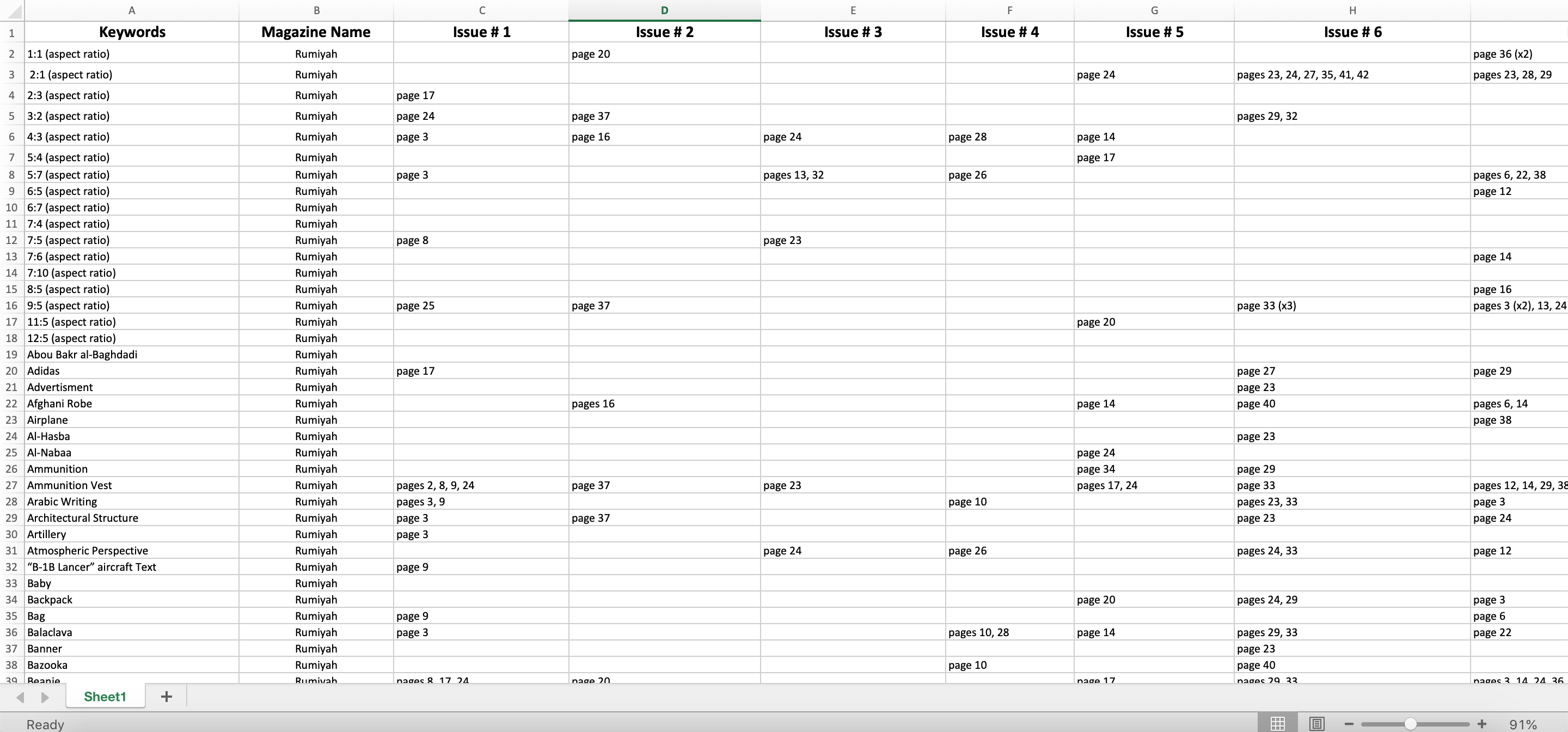
I then added all the keywords in an Excel Sheet in order to see the reoccurrence of each keyword. And for this reason I had to go over all the keywords multiple times to make sure they are as consistent as possible. Figure 1.4 is a screenshot of part of the Excel Sheet that consists of all the keywords, which issue they were in, and which page.
Some Explanation about the Photography Techniques I looked at in order to get to the results I showed above
Camera Angle is the apparent distance and angle from which the camera views and records the subject. There are a number of camera angles, such as:
- High-angle shot (HA) is a shot in which the camera is physically higher than the subject and is looking down upon the subject. The high angle shot can make the subject look small or weak or vulnerable
- Low-angle shot(LA) is taken from below the subject and has the power to make the subject look powerful or threatening.
- Bird’s-eye view or a Bird’s eye shot is taken directly above the scene to establish the landscape and the actors relationship to it.
- Worm’s-eye view is a shot that is looking up from the ground, and is meant to give the viewer the feeling that they are looking up at the character from way below and it is meant to show the view that a child or a pet would have.
- Eye-level camera angle, neutral shot or eye-level (EL) shot has little to no psychological effect on the viewer. This shot is when the camera is level or looking straight on with the subject.
- Point of view shot (POV) shows the viewer the image through the subject’s eye. Some POV shots use hand-held cameras to create the illusion that the viewer is seeing through the subject’s eyes.
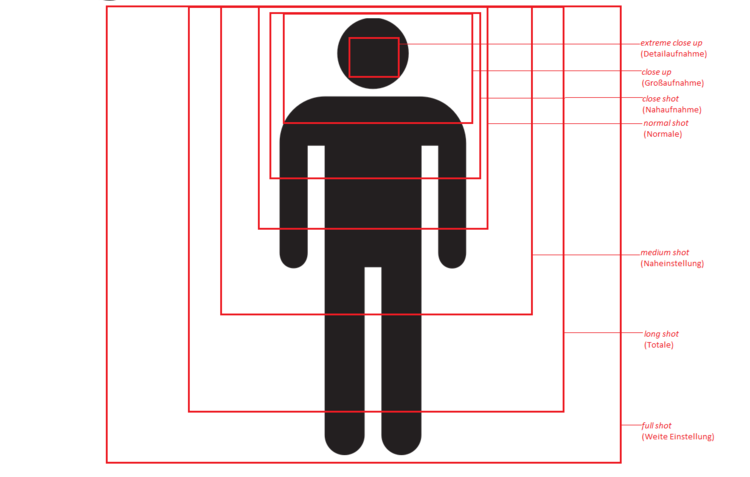
Types of portraits
(http://myportraithub.com/different-types-of-portrait-photography/http://learnmyshot.com/9-fundamental-styles-of-portrait-photography/)
On the basis of subject:
- Candid Portrait are the one where the subject may be aware or unaware of presence of a photographer. However, in such portraits, the photographer does not have much liberty to change the environment or emotions of the person being photographed. Things are natural and spontaneous.
- Environmental Portrait normally focuses on the relation of the subject with his environment. The relation between the subject and his environment is more dominant than the facial expressions.
- Posed Portrait (Traditional Portrait) is simply a portrait where the subject is fully aware of photographer’s presence and selects a certain body posture for the picture.
- Formal Portrait is a posed portrait prepared for business or other formal occasions. Abstract Portrait are created with a purpose of creating art and not based on realistic representation of a person. Collage or digital manipulation is often used.
- Conceptual Portrait refers to images where concept adds a fourth dimension. The hidden meaning of the concept will leave the viewer guessing as it is often open for interpretation.
- Surreal Portrait are created to emphasize the other reality. A depiction of a person’s interpreted subconscious mind.
- Lifestyle Portrait refers to portraits where emphasis is given to suggest the “style of living” of the individuals depicted. Technically, it is a combination of environmental portrait and candid portrait. More weight is given to communicate the feeling of life experience of the subject.
- Glamour Portrait refers to portraits where emphasis is given to highlight the sexy romantic appeal of the subject.
On the basis of number of people in the frame:
- Individual Portrait
- Couple Portrait
- Group Portrait
On the basis of shot/frame:
- Close-ups
- Facial Shots
- Upper Body Shot
- Full Body Shot
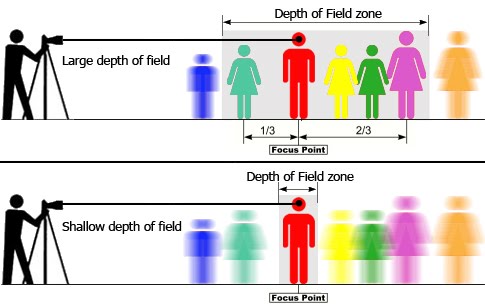
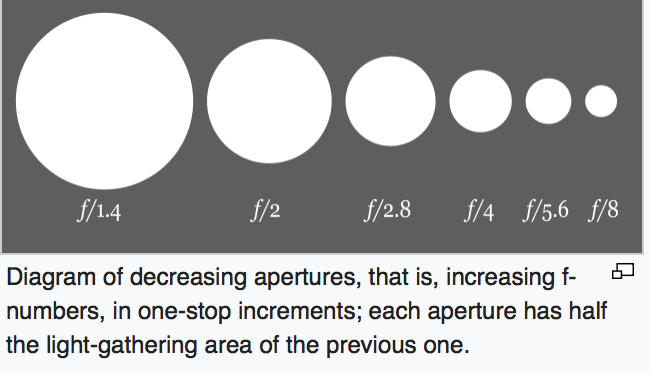
Aperture and Depth of Field (DoF)
Reducing the aperture diameter (increasing the f-number) increases the Depth of Field
Aspect Ratio
(https://digital-photography-school.com/aspect-ratio-what-it-is-and-why-it-matters/)
Why does aspect ratio matter? It’s all to do with the relationship of the main subject to the sides of the frame, and the amount of empty space you end up with around the subject. An awareness of the characteristics of the aspect ratio of your particular camera can help you compose better images. It also helps you recognise when cropping to a different aspect ratio will improve the composition of your image.
Aspect ratio describes the relationship between the width and height of an image. It’s written as a figure, in this form = width : height (width always comes first).
Aspect ratio = Original Width ÷ Original Height
Aspect Ratios
- Landscape
3:2
4:3
5:4
7:6
16:9 - Portrait
2:3
3:4
4:5
6:7
9:16 - Square
1:1
Golden Ratio
Phi Grid
The Rule of Thirds






.png)
